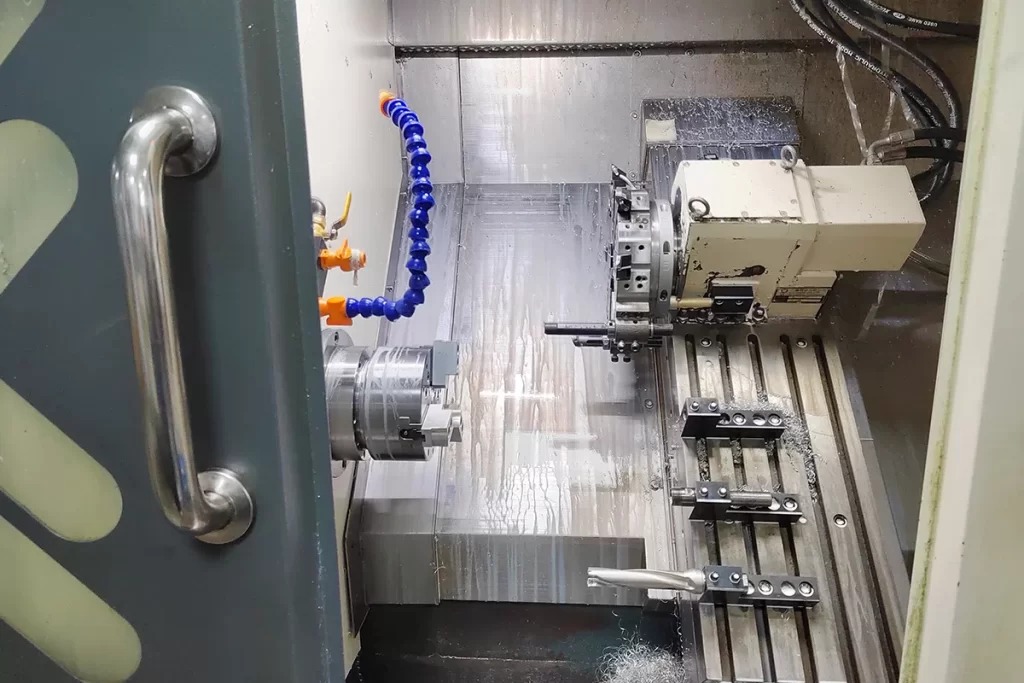
What is CNC Machining? – A Comprehensive Overview
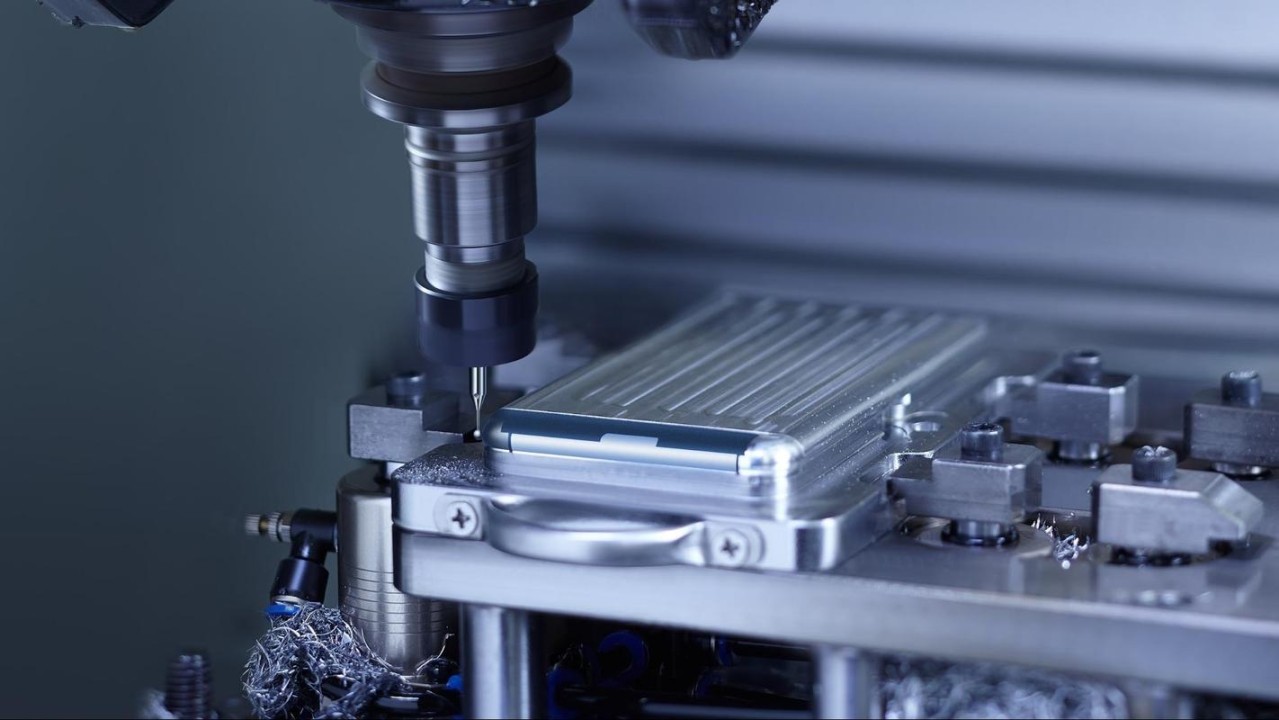
CNC machining, short for computer numerical control machining, stands as a widely adopted manufacturing technique that employs automated, high-speed cutting tools to shape designs from metal or plastic stock. This method utilizes various standard CNC machines, including 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines, lathes, and routers. The approach to cutting CNC parts may differ, as the workpiece might stay stationary while the tool moves, or vice versa, or both may move together.
Proficient machinists operate CNC machines by programming tool paths based on the final part’s geometry, which is typically defined by a CAD (computer-aided design) model. CNC machines exhibit exceptional precision and repeatability, enabling the fabrication of custom machined parts from nearly any metal alloy or rigid plastic. This versatility makes CNC machining suitable for diverse industries such as aerospace, medical, robotics, electronics, and industrial applications. Fuyu offers CNC services and provides custom CNC quotes on a wide range of materials, encompassing over 40 options from basic aluminum and acetal to advanced titanium and engineered plastics like PEEK and Teflon.
Materials for CNC Machining of Metals
Aluminum Alloys for CNC Machining
Aluminum stands out as a lightweight metal renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, rendering it highly suitable for applications prioritizing strength while keeping mass to a minimum. Aluminum alloys come in various compositions, each identified by the primary alloying element, typically denoted by the first number in their classification. Aluminum ranks among the most prevalent materials utilized across aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors, owing to its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, malleability, and overall adaptability. For a quote on CNC machining services for aluminum, contact Fuyu.
Aluminum 6061
Aluminum 5052
Aluminum 2024
Aluminum 6063
Aluminum 7050
Aluminum 7075
CNC Machining of Copper Alloys
Copper, identified as Cu with an atomic number of 29 on the periodic table, boasts exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, second only to silver. Commercially available copper is typically comprised of over 99% purity, with the remaining 1% consisting of impurities like oxygen, lead, or silver. Copper is renowned for its superior electrical and thermal conductivity, along with remarkable resistance to corrosion and inherent antimicrobial properties. Industries such as power, automotive, medical, and aerospace leverage copper precisely for these distinctive characteristics. Submit your copper CNC machining project for a quote to Fuyu.
Copper 101
Copper C110
CNC Machining of Bronze Alloys
Bronze is formulated by blending copper with tin up to approximately 35% and lead up to 8%. The addition of lead alloy, a soft metal, enhances its machinability. Bronze finds extensive use in applications such as bearings and marine components like pumps and fittings requiring corrosion resistance against seawater. While its mechanical properties may not match those of some other machinable metals, bronze is well-suited for low-stress components manufactured via CNC machining.
Bronze, along with brass and various copper alloys, boasts crucial electrical, mechanical, and corrosion-resistant attributes. Notably, bronze exhibits exceptional machinability, rated at 100% on the machinability index. Moreover, it offers low-friction properties, making it ideal for parts subjected to continuous frictional contact.
Request an instant quote for your custom CNC machined bronze parts today.
Copper C932
CNC Machining of Brass Alloys
Brass encompasses a broad spectrum of copper-zinc alloys distinguished by varying zinc content and the inclusion of other alloying elements like lead, aluminum, and iron. Its copper content imparts thermal and electrical conductivity, while also contributing to good wear resistance. The addition of lead enhances machinability, rendering brass the most machinable among copper alloys.
Brass stands as a versatile copper alloy that not only inherits some of copper’s advantages but also enhances certain attributes. Mechanically stronger and exhibiting lower friction than copper, brass also offers superior corrosion and wear resistance. These properties render CNC machining of brass ideal for mechanical applications demanding corrosion resistance, such as those prevalent in the marine industry.
Purchase Custom CNC Machined Brass Parts Today.
Copper 260
Copper 360
CNC Machining of Stainless Steel Alloys
The distinctive feature of stainless steel lies in the incorporation of chromium into its alloys. All compositions of stainless steel contain a minimum of 10.5% chromium, rendering them more resistant to corrosion. Various grades of stainless steel incorporate different alloying elements to enhance corrosion resistance, heat treatability, and machinability. It’s important to note that heat treatment can significantly impact the mechanical properties of the metal.
Stainless steels can be categorized based on their crystalline structure, including Austenitic, Ferritic, Martensitic, and Duplex:
• Austenitic stainless steel, such as the 300- and 200-series, exhibit high formability and do not work harden. They remain non-magnetic when annealed.
• Ferritic stainless steels are magnetic and offer superior thermal conductivity compared to austenitic stainless steel. They cannot be hardened through heat treatment.
• Martensitic stainless steel, like grades 416 and 420, can be hardened through various aging or heat treatment methods.
• Duplex stainless steel, also referred to as austenitic-ferritic, is highly specialized for enhanced corrosion resistance. Duplex steels find common use in industrial and architectural applications.
Given its versatility, stainless steel in some form finds extensive application across every industry.
Nitronic 60 (218 SS)
Stainless Steel 15-5
Stainless Steel 17-4
Stainless Steel 18-8
Stainless Steel 303
Stainless Steel 316/316L
Stainless Steel 416
Stainless Steel 410
Stainless Steel 420
Stainless Steel 440C
CNC Machining of Steel Alloys
Steel is an alloy of iron containing around 1% carbon, with additional small amounts of alloying elements like molybdenum and chromium often added to enhance its properties. It presents an excellent balance between cost and functionality due to its ease of machining and welding. However, steel is prone to oxidation over time and requires surface treatments for protection.
As one of the most ubiquitous manufacturing materials, steel finds applications across all major industries, ranging from construction to automotive. Its cost-effectiveness and advantageous properties render it a highly versatile material. Below are some variants of mild steel and high-strength steel available for CNC machining through Fuyu.
Get Your Instant Quote for CNC Machining Steel
Steel 1018
Steel 1215
Steel 4130
Steel 4140
Steel 4140PH
Steel 4340
A2 Tool Steel
O1 Tool Steel
CNC Machining of Titanium Alloys
Titanium (Ti on the periodic table) is a lightweight metal renowned for its wide array of beneficial properties, including corrosion resistance and strength retention even at extreme temperatures. It is available in both pure form and as alloys. It’s worth noting that even pure titanium contains trace amounts (less than 1%) of iron and oxygen. Advanced alloys greatly enhance titanium’s overall strength.
Titanium is an advanced material prized for its exceptional corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and impressive strength-to-weight ratio. These remarkable properties make it a preferred choice for addressing various engineering challenges encountered in the medical, energy, chemical processing, and aerospace sectors.
Obtain Your Instant Quote for Titanium Machining.
Titanium (Grade 2)
Titanium (Grade 5)
CNC Machining of Zinc Alloys
Zinc (Zn on the periodic table) is a commonly used non-magnetic metal frequently alloyed with aluminum, magnesium, and copper. This category of zinc alloys is known as Zamak, originating from the German acronym “Zink, Aluminium, Magnesium, and Kupfer.” Typically supplied in ingot form, these alloys are extensively utilized in die-casting applications. Zinc boasts remarkable damping capacity, high ductility, and long-term dimensional stability.
Zinc alloy metals are among the most cost-effective materials available. Despite their affordability, they offer commendable mechanical strength, ease of machining, and excellent resistance to mechanical shocks. Complex components are often initially die-cast and subsequently machined to add critical features, thereby reducing overall CNC machining time and costs. The automotive industry extensively employs CNC machined zinc alloys.
Explore CNC Machining of Zinc Alloys Today
Zinc Alloy
Plastic Materials for CNC Machining
ABS: A high-strength engineering plastic utilized in numerous commercial products.
Acrylic: A transparent, glass-like plastic renowned for its good wear and tear properties, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Delrin (Acetal): A resin characterized by its excellent moisture resistance, high wear resistance, and low friction.
HDPE High-density polyethylene, offering moisture and chemical resistance along with impressive impact strength. Ideal for outdoor usage and the fabrication of watertight containers or seals.
Nylon 6/6: Provides enhanced mechanical strength, rigidity, and stability under heat, as well as resistance to chemicals.
PC (Polycarbonate): Boasting nearly double the tensile strength of ABS, polycarbonate exhibits superior mechanical and structural properties. Widely employed in automotive, aerospace, and other industries requiring durability and stability.
PEEK: Known for its exceptional tensile strength, PEEK serves as a lightweight alternative to metal parts in high-temperature, high-stress applications. Exhibits resistance to chemicals, wear, and moisture.
Polypropylene: Features excellent electrical properties and minimal moisture absorption, enduring light loads across a wide temperature range. Suitable for parts requiring chemical or corrosion resistance.
PTFE (Teflon): Outperforms most plastics in terms of chemical resistance and performance in extreme temperatures. Resistant to most solvents and serves as an outstanding electrical insulator.
PVC Polyvinyl chloride (Type 1): stands out for its high chemical resistance, making it a preferred choice for environments exposed to liquids or necessitating electrical insulation.
Available Surface Treatment
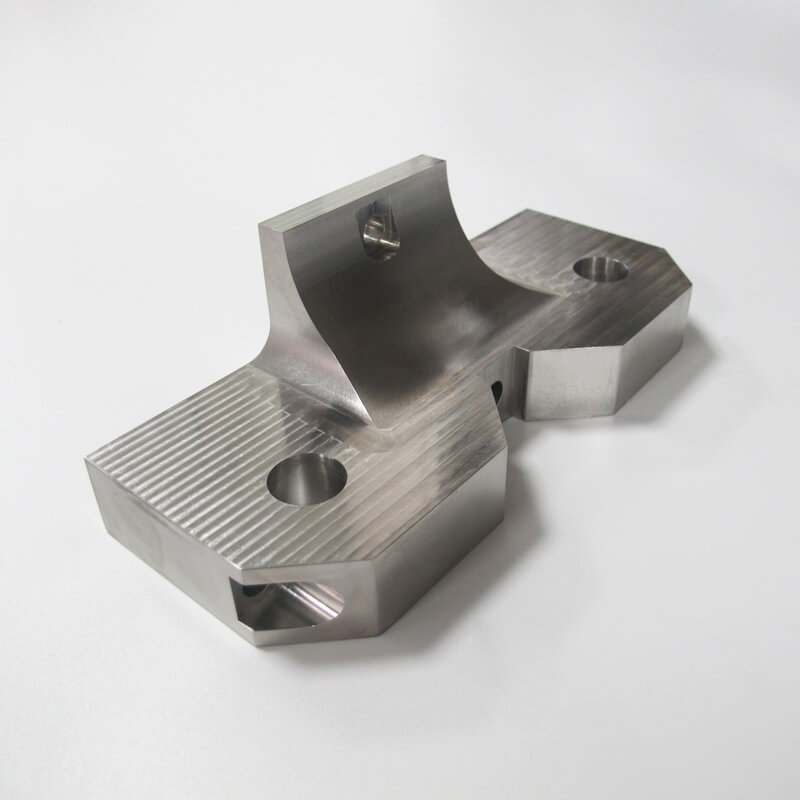

Standard (As-Milled)
This finish option offers the quickest turnaround time. Machined parts retain visible tool marks and may have sharp edges and burrs, which can be eliminated upon request. The surface finish achieved through CNC machining is akin to a 125 uin Ra finish.
Bead Blast
The part surface undergoes media blasting, typically using glass bead, resulting in a smooth, matte appearance.
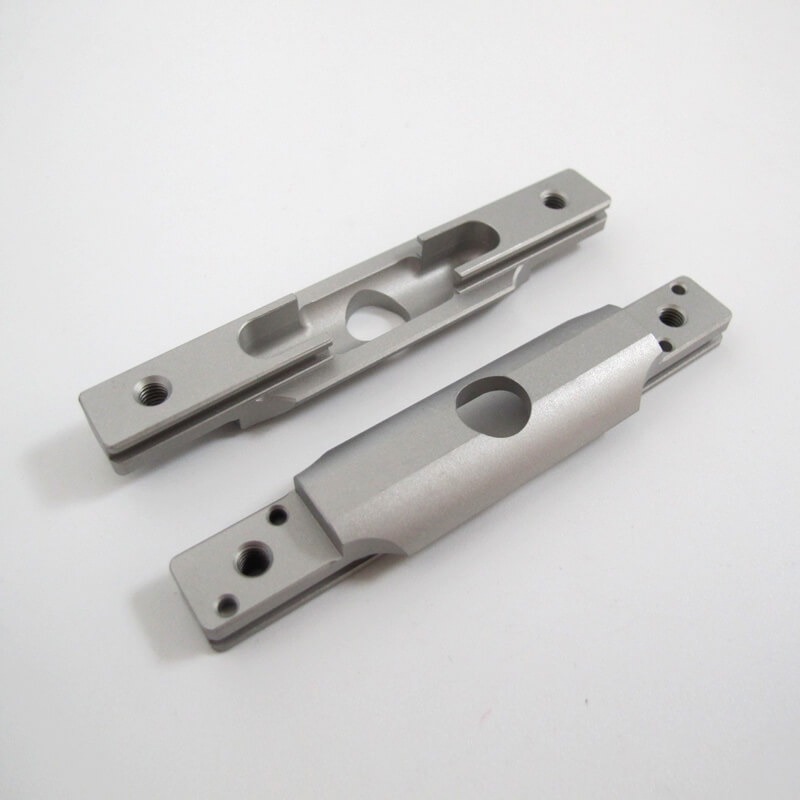
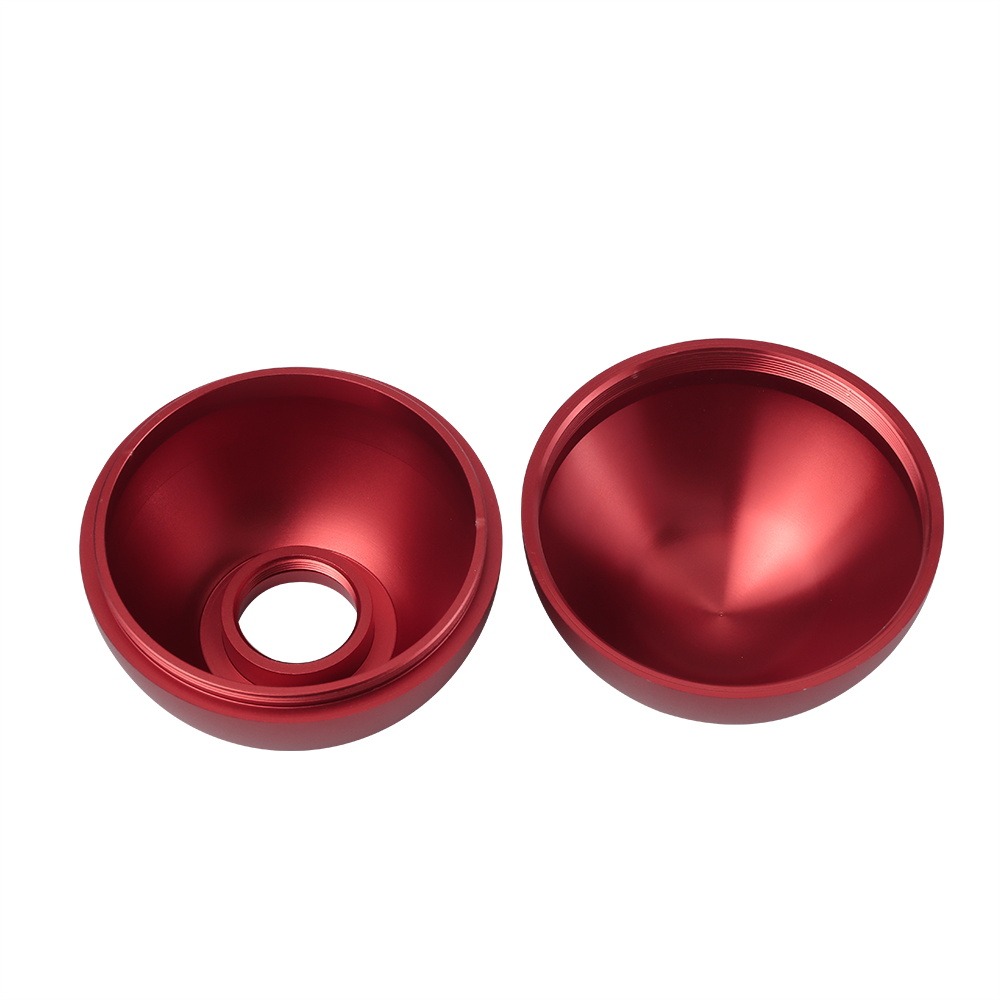


Anodized (Type II Or Type III)
Type II creates a corrosion-resistant finish and allows for anodizing in various colors—common choices include clear, black, red, and gold, typically associated with aluminum. Type III is thicker and provides a wear-resistant layer in addition to corrosion resistance, commonly seen in aerospace applications.
Powder Coat
This process involves spraying powdered paint onto a part followed by baking in an oven. The result is a robust, wear- and corrosion-resistant layer, surpassing standard painting methods. A wide array of colors are available to achieve the desired aesthetic.


Tumbled
A batch-based process that utilizes vibrating media to remove sharp edges and burrs from CNC parts. Tumbling can also eliminate machine marks on exterior surfaces. Parts exceeding 8” may necessitate manual review.
Titanium Anodize
A surface finish for titanium as per AMS-2488 Type 2 specification, also known as Tiodize. This finish enhances fatigue strength and wear resistance, commonly found in aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Non-pigmented titanium anodize finishes result in a dulled shine.


PTFE Impregnated Hard Anodize
A hard coat anodize process incorporating PTFE to create a self-lubricating, dry contact surface with the protective properties of Type 3 hard coat. Suitable for aluminum alloys or titanium, it prolongs product service life and adheres to the AMS-2482 Type 1 Hard Coat Anodizing with Teflon (Non-Dyed) standard.
Chem Film (Chromate Conversion Coating)
Provides corrosion resistance and good conductivity properties, serving as a base for paint applications. May impart a yellow/golden hue to the surface. Adds minimal thickness, approximately 0.00001”-0.00004”, and adheres to the MIL-DTL-5541, TYPE I/II standard.


Passivation
Enhances corrosion resistance for 200 and 300 series and precipitation-hardened corrosion-resistant steels. Adds negligible thickness, around 0.0000001”, and conforms to ASTM A967, AMS-QQ-P-35, MIL-STD-171, ASTM A380, or AMS 2700 standards.
Electropolishing
An electrochemical process that cleans steel parts to reduce corrosion and enhance appearance by brightening the metal. Removes approximately 0.0001”-0.0025” of metal and complies with ASTM B912-02 standard.


Electroless Nickel Plating
Delivers a uniform nickel coating offering protection from corrosion, oxidation, and wear on irregular surfaces. Results in a brighter finished part, with thickness starting at .0001” and conforming to MIL-C-26074 standard.
Silver Plating
Silver plating offers high solderability and electrical conductivity but may tarnish over time. Complies with AMS QQ-S-365D standard, with a thickness ranging from 0.00002” to 0.0003”.


Gold Plating
Provides good corrosion and tarnish resistance along with excellent solderability. Default application specification is MIL-G-45204 and ASTM B488, CLASS 00, 0, OR 1, with a thickness ranging from 0.00002″ to 0.00005″.
Zinc Plating
Delivers a uniform zinc coating offering protection from corrosion, oxidation, and wear on irregular surfaces, adhering to ASTM B633-15 standard.

Custom Can’t find the finish you require? Submit an RFQ, and we’ll explore a finishing process tailored to your needs.
Industries Benefitting from High-Volume CNC Machining
Highlighted below are the key industries that leverage high-volume CNC machining effectively:
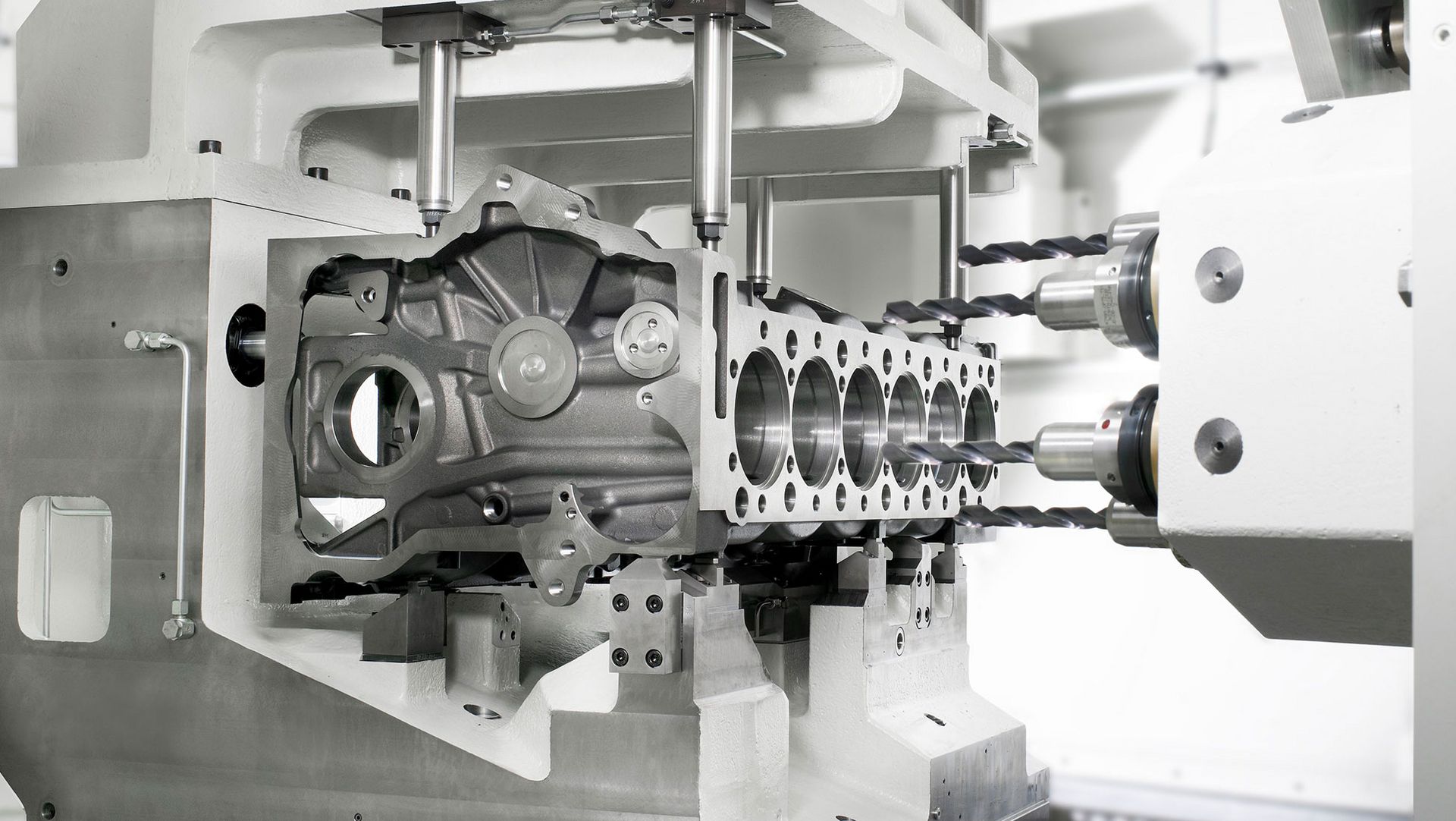
Automotive Sector
High-volume CNC machining plays a pivotal role in producing precise and high-quality components for various automotive applications, including engine parts, transmission components, brake systems, and intricate interior and exterior components. The automotive industry relies on the efficiency and consistency of CNC machining to meet mass production demands while upholding rigorous quality standards.
Aerospace Field
High-volume CNC machining is indispensable in the aerospace industry for manufacturing critical components such as aircraft engine parts, landing gear components, structural elements, and avionics parts. CNC machines offer the versatility to work with aerospace-grade alloys and composites, making them vital for this technologically advanced and safety-critical sector.

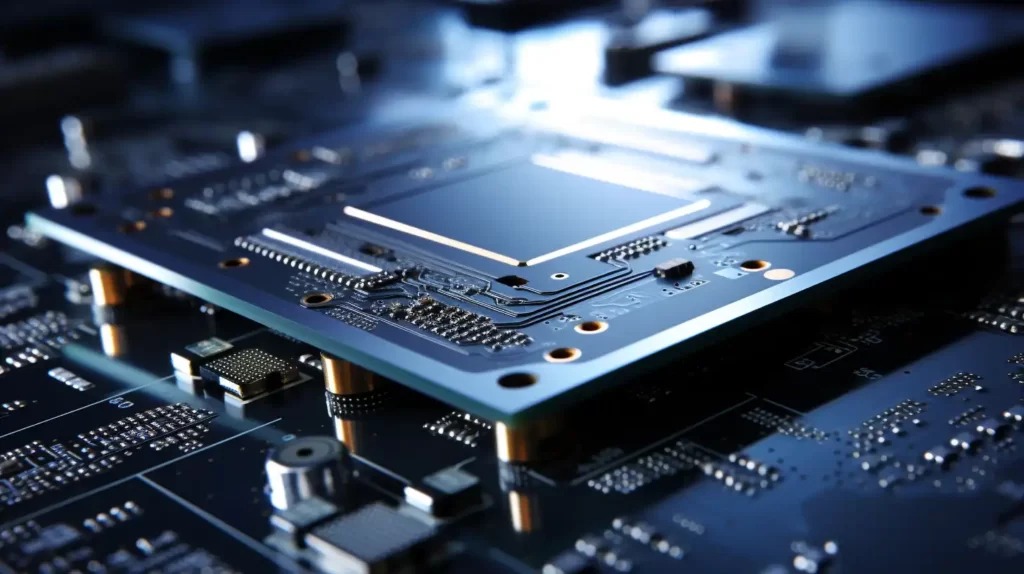
Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry requires intricate and miniaturized components in large quantities. High-volume CNC machining provides the precision necessary for manufacturing complex electronic parts like connectors, heat sinks, housings, and electronic enclosures. CNC machines excel in producing precise features and tolerances crucial for the electronics sector, where minor deviations can impact performance significantly.
Medical Sector
High-volume CNC machining is extensively used in producing medical devices and components such as surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, prostheses, and dental components. CNC machining ensures that medical devices meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining exceptional accuracy and quality standards.

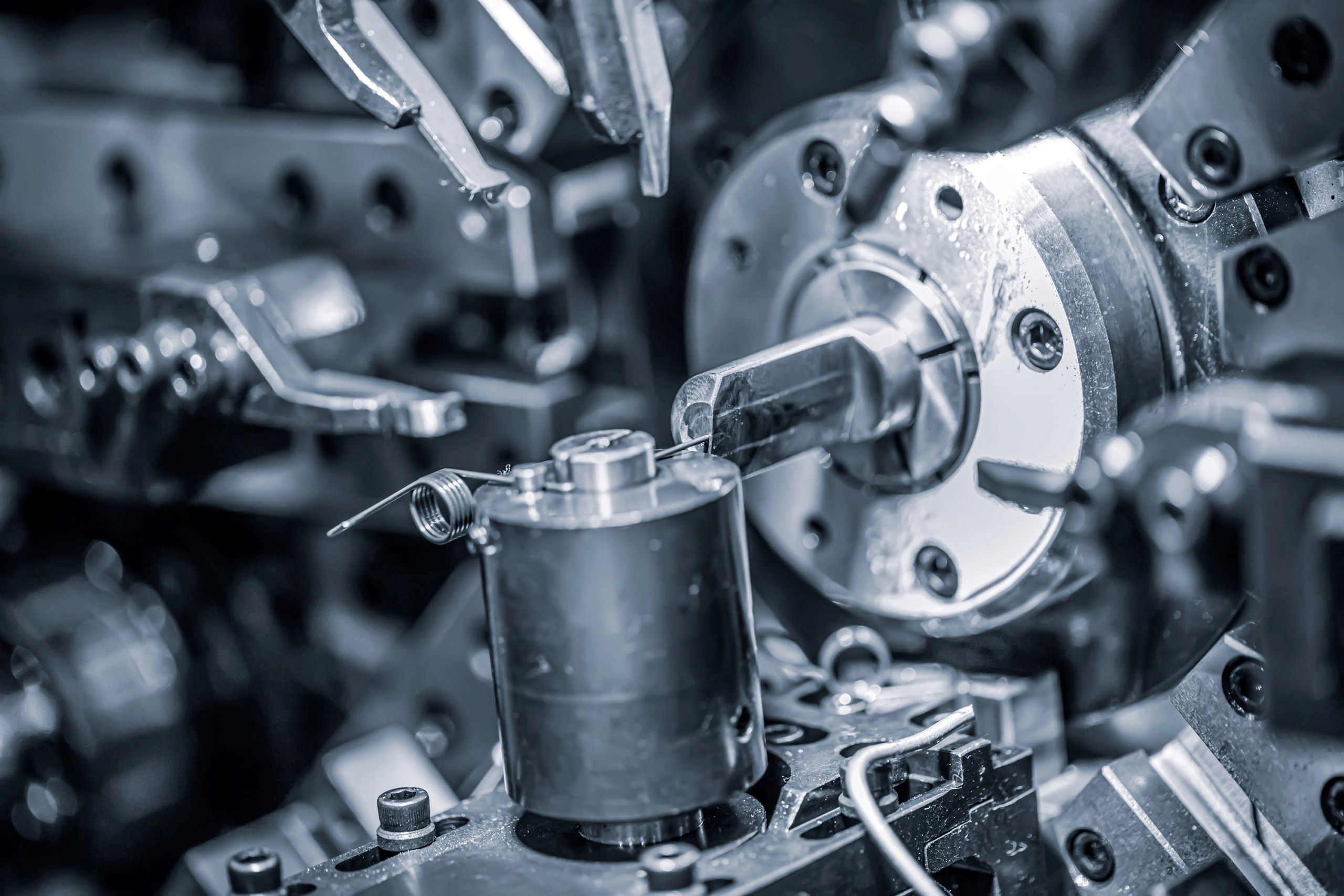
Industrial Applications
High-volume CNC machining finds application in producing industrial machinery parts, automation components, hydraulic and pneumatic systems, and tooling. CNC machining’s versatility in handling a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics, makes it suitable for various industrial applications.
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics sector, high-volume CNC machining is crucial for producing components for smartphones, laptops, gaming consoles, and other electronic devices. CNC machines facilitate the creation of precise and intricate designs, ensuring seamless functionality and aesthetic appeal in consumer electronics products.


Energy and Power Generation
The energy and power generation industries benefit from high-volume CNC machining for manufacturing parts for turbines, generators, compressors, and other equipment used in power plants and renewable energy installations.
Alternatives to High-Volume CNC Machining Services
For clients exploring alternatives to high-volume CNC machining services, there are several manufacturing processes to consider, each offering unique strengths and applications. Some notable alternatives include:
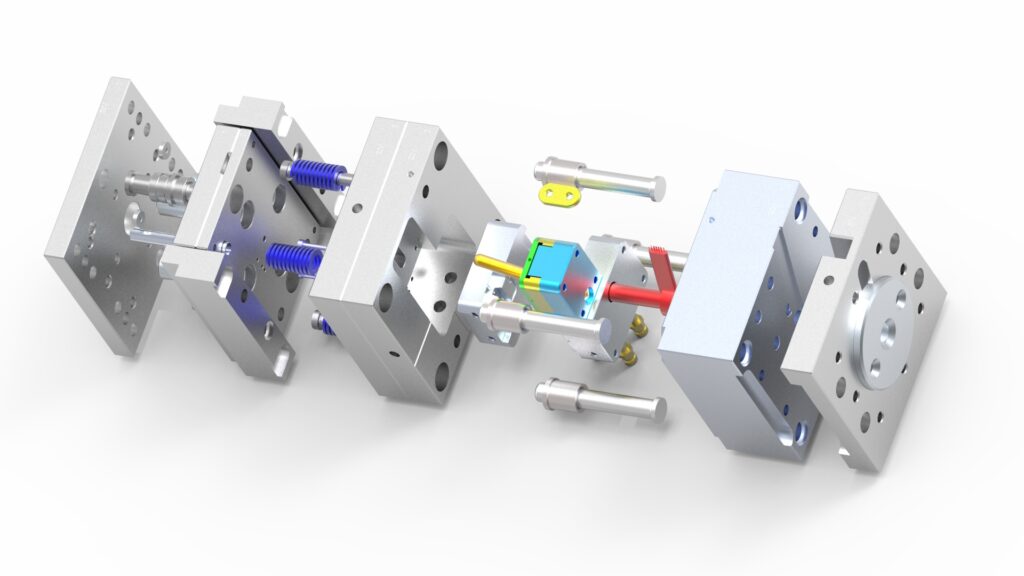
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely adopted manufacturing method for producing high volumes of plastic parts with precision and consistency. It is an efficient process for mass-producing intricate and complex geometries, making it well-suited for industries such as automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and medical devices.
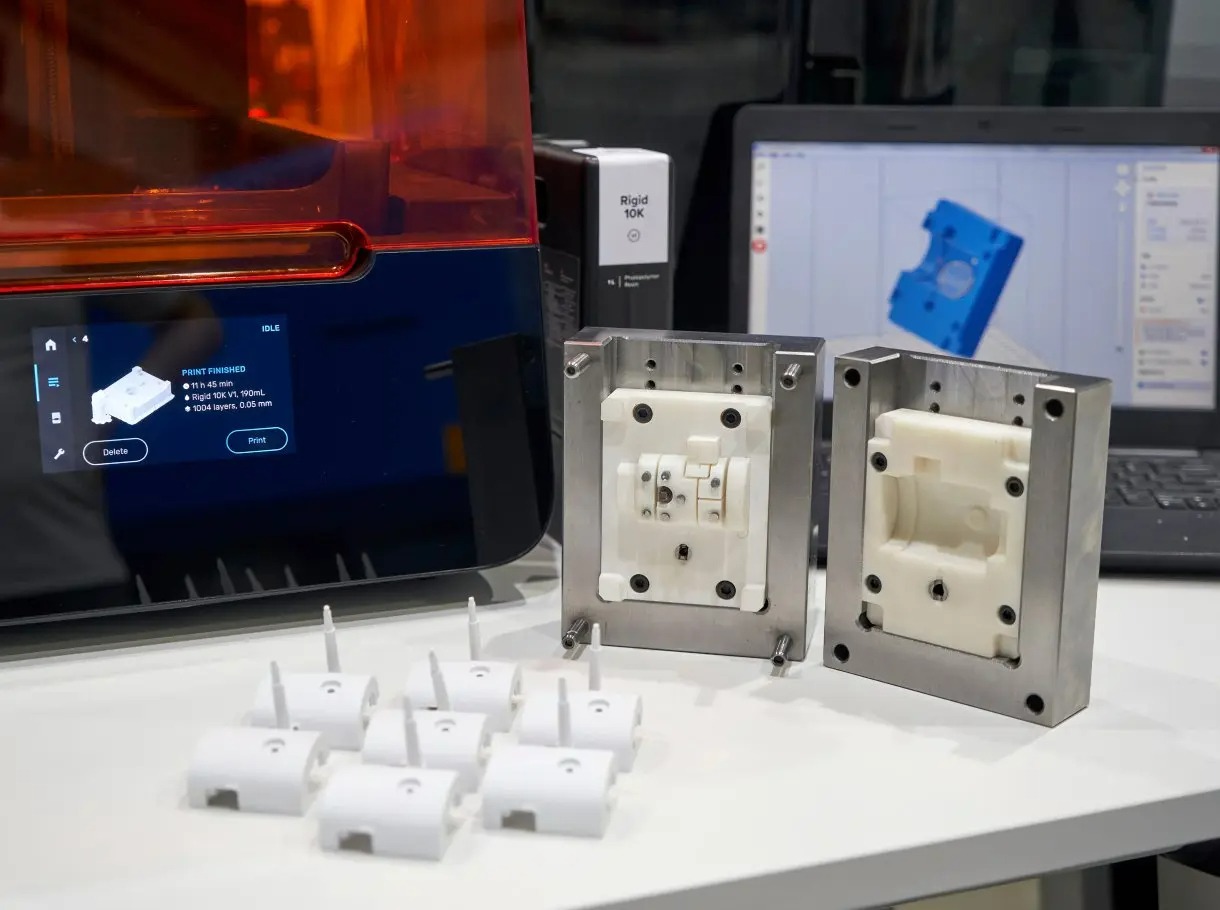

3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, constructs objects layer by layer from digital 3D models. While traditionally used for prototyping and small batches, advancements in 3D printing now enable limited high-volume production. It is particularly beneficial for highly customized and unique parts or when rapid iteration and design changes are required.
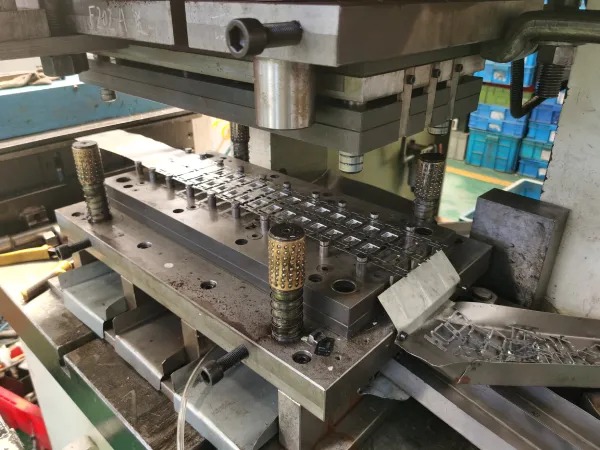

Stamping
Stamping involves shaping sheet metal into desired forms using presses and dies. It is commonly employed to manufacture large quantities of parts with consistent dimensions, such as automotive body panels, electronic enclosures, and metal brackets. Stamping is renowned for its speed and cost-effectiveness in high-volume production runs.
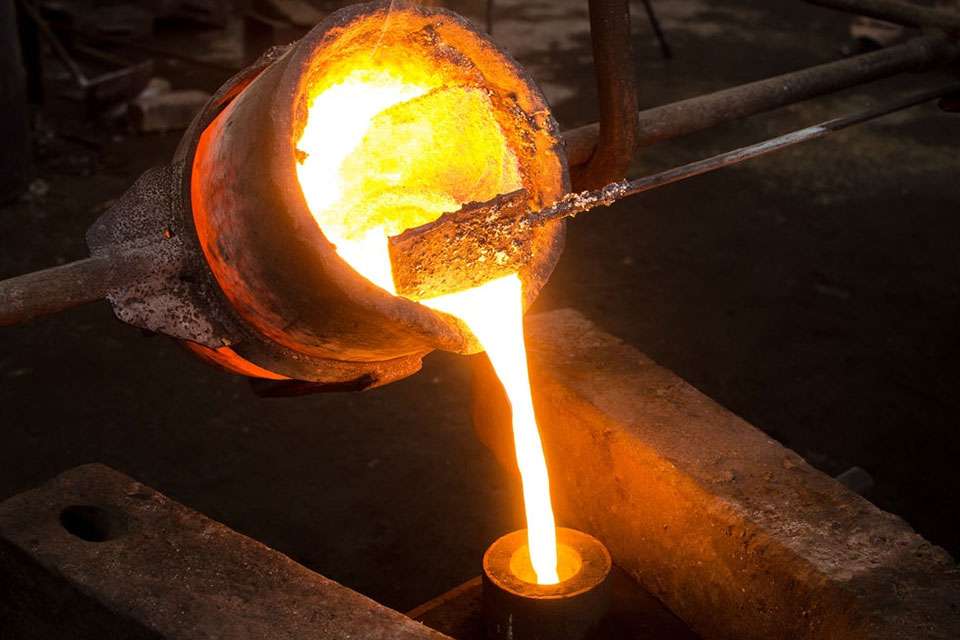

Casting
Casting is a process wherein liquid metal, plastic, or other materials are poured into a mold to create a solid object. It is frequently utilized for producing complex metal parts in large volumes. Die casting, investment casting, and sand casting are common casting techniques employed for the large-scale production of automotive components, industrial machinery parts, and more.
Advantages and Challenges of CNC Machining
Advantages of CNC Machining
CNC milling and turning processes offer exceptional accuracy and repeatability. Tight tolerances ranging between +/-0.001″ – 0.005″ can be achieved, depending on specific requirements. CNC machines can be programmed to operate reliably 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, facilitating on-demand part production.
Utilizing standard tooling, CNC machining services are particularly beneficial for creating one-off parts or custom CNC parts, such as replacements for legacy components or specialized upgrades for customers. It is also possible to scale single-part production to runs exceeding 10,000 units. Depending on the quantity, size, and complexity, CNC machined parts can be turned around in as little as one day. With shipping and delivery, deadlines can be met within a week.
Another significant advantage of CNC technology is its ability to retain desirable mechanical properties of the material being machined. Unlike processes such as injection molding or additive manufacturing, which thermally transform materials, CNC machining cuts away bulk material while preserving its mechanical properties. CNC milling and turning can handle more than 50 industrial-grade metals, alloys, and plastics, including aluminum, brass, bronze, titanium, stainless steel, PEEK, ABS, and zinc. The only requirement for CNC machining is that the material has adequate hardness for fixturing and cutting.
Challenges of CNC Machining
One challenge when leveraging the high performance of CNC machining processes is that geometric complexity often comes with a cost. Simple, robust parts are best suited for CNC milling and turning, as there are design limitations due to tool access. However, the extent of this limitation is relative to the number of axes on the machine. Generally, the more axes used, the more complex features can be achieved.
Another challenge is the initial startup costs of CNC machining, which can be significant. Trained professionals are required for setup, tool loading, and programming on CNC mills and lathes. However, this cost is fixed, and by utilizing the same setup for multiple parts, it becomes more economical. Cost savings can also be achieved by minimizing part repositioning. Machining at 5-axis and above can sometimes be more cost-effective for multi-faceted geometries, as it eliminates the need for manual repositioning of the part.
Wire EDM machining can be slower and more expensive compared to other processes, and the range of materials that can be used is limited as they must be electrically conductive.
CNC Machining Tolerances
| Feature | Description |
| Maximum Part Size | Milled parts up to 80” x 48” x 24” (2,032 x 1,219 x 610 mm). Lathe parts up to 62” (1,575 mm) length and 32” (813 mm) diameter. |
| Standard Lead Time | 14-20 business days |
| General Tolerances | Tolerances on metals will be held to +/- 0.005″ (+/- 0.127 mm) in accordance with ISO 2768 unless otherwise specified. Plastics and composites will be +/- 0.010”. |
| Precision Tolerances | Fuyu can manufacture and inspect to tight tolerances, including sub +/- 0.001″ tolerances, per your drawing specifications and GD&T callouts. |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.020” (0.50 mm). This may vary depending on part geometry and chosen material. |
| Threads and Tapped Holes | Fuyu can accommodate any standard thread size. We can also machine custom threads; these will require a manual quote review. |
| Edge Condition | Sharp edges are broken and deburred by default |
| Surface Finish | The standard finish is as-machined: 125 Ra or better. Additional finishing options can be specified when getting a quote. |
FAQs – What is CNC Machining?
How does CNC machining work?
CNC machining operates through subtractive processes, meaning material is shaped into its final form by removing excess material. This includes drilling holes, creating slots and pathways, and shaping metal stock into various forms with different tapers, diameters, and contours.
In contrast to additive manufacturing methods, where material is added and layered to form a shape, CNC machining achieves shapes by removing material. It also differs from injection molding, where material is injected into a mold in a different state and shaped into a specific form.
CNC machining is highly versatile and compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, foam, and composites. This versatility has made CNC machining a preferred choice across industries, enabling efficient and precise fabrication of products.
What are your tolerances for machined parts?
For most geometries in metals, our local tolerances are +.005”/- .005”, while for plastics, it’s +/- 0.010″. These tolerances may vary for large parts, especially when maintaining flatness after heat treatment. Regarding surface finish requirements, our “As Milled” finish adheres to a minimum 125 surface finish for CNC parts.
What are your CNC machining & turning capabilities?
At Fuyu, we possess extensive CNC capabilities in our machining shop. Here are some guidelines for machine sizes:
5 Axis Machining: Up to 26″
4 Axis Machining: Up to 36″
3 Axis Machining: Up to 60″
Dual Spindle Lathes: With a 32″ Swing, 18″ Max Diameter, and 8″ Chuck
Wire EDM: With a part depth of 18″
Do you offer Quick-Turn CNC Machining?
Yes, Fuyu provides quick lead times for quick-turn parts, with many parts available within 7-15 days. We offer an expedite option, and our team collaborates closely with you to meet urgent deadlines.
Feel free to reach out to us with any further inquiries or to discuss your specific prototyping requirements!


