Custom Online CNC Machining Services
Fuyu offers customized online CNC machining services tailored to the needs of engineers, product developers, and designers. Leveraging our AS9100D certified machine shops, we provide comprehensive solutions for all custom designs, regardless of complexity. Our service encompasses rapid machining, small-batch production, and high-volume manufacturing, ensuring end-to-end support for all orders.
Why Contact Fuyu for Custom Online CNC Machining Services?


CNC machining, or computer numerical control machining, is a highly automated manufacturing process that utilizes high-speed cutting tools to create precise designs from metal or plastic stock. Standard CNC machinery encompasses 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines, lathes, and routers. The machining process can involve various configurations, such as stationary workpieces with moving tools, rotating and moving workpieces with stationary tools, or simultaneous movement of both cutting tools and workpieces.
Skilled machinists operate CNC machines by programming tool paths based on the geometry of the desired machined parts, often derived from computer-aided design (CAD) models. CNC machines excel in precision and repeatability, making them capable of machining nearly any metal alloy or rigid plastic with exceptional accuracy. This versatility makes custom machined parts suitable for diverse industries, including aerospace, medical, robotics, electronics, and industrial sectors.
Fuyu offers comprehensive CNC services and custom CNC quoting for a vast selection of materials, encompassing both common materials like aluminum and acetal, as well as advanced materials such as titanium and engineered plastics like PEEK and Teflon.
Custom CNC Machining Services: Machining, Turning, Milling, and Routing
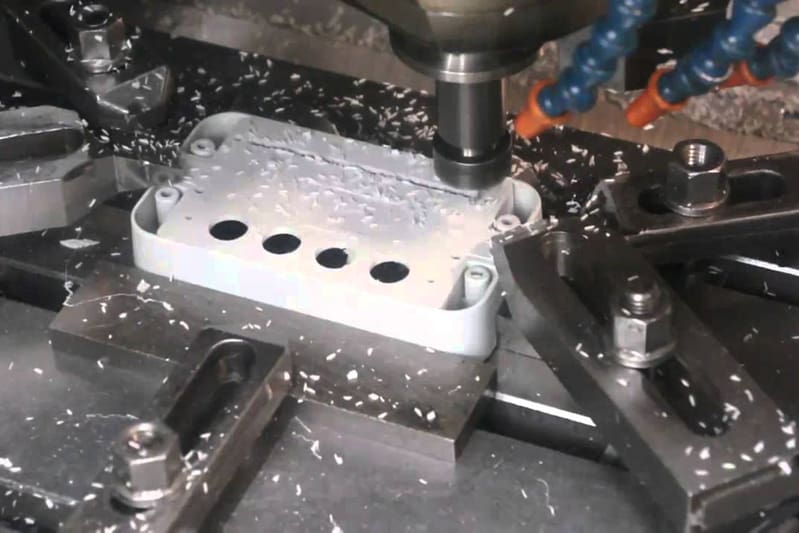

Custom CNC Milling Services
CNC milled prototypes and production parts in days | AS9100D | ISO 9001:2015 | ISO 13485 | IATF 16949:2016 | ITAR Registered | Free standard shipping on all US orders
Learn more abour Comprehensive Guide To CNC Milling
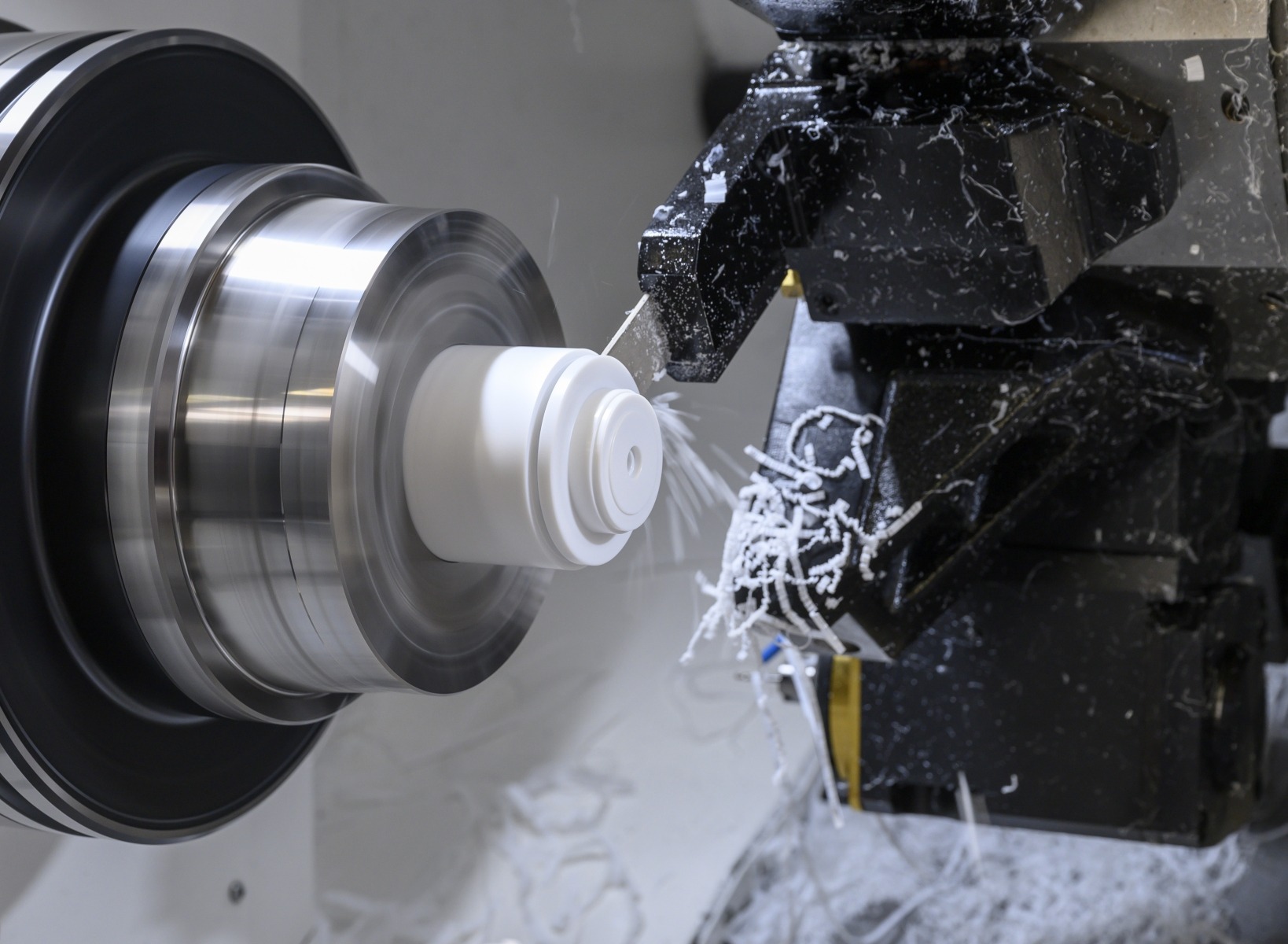

CNC Turning Service
CNC turned prototypes and production parts in days | AS9100D | ISO 9001:2015 | ISO 13485 | IATF 16949:2016 | ITAR Registered | Free standard shipping on all US orders
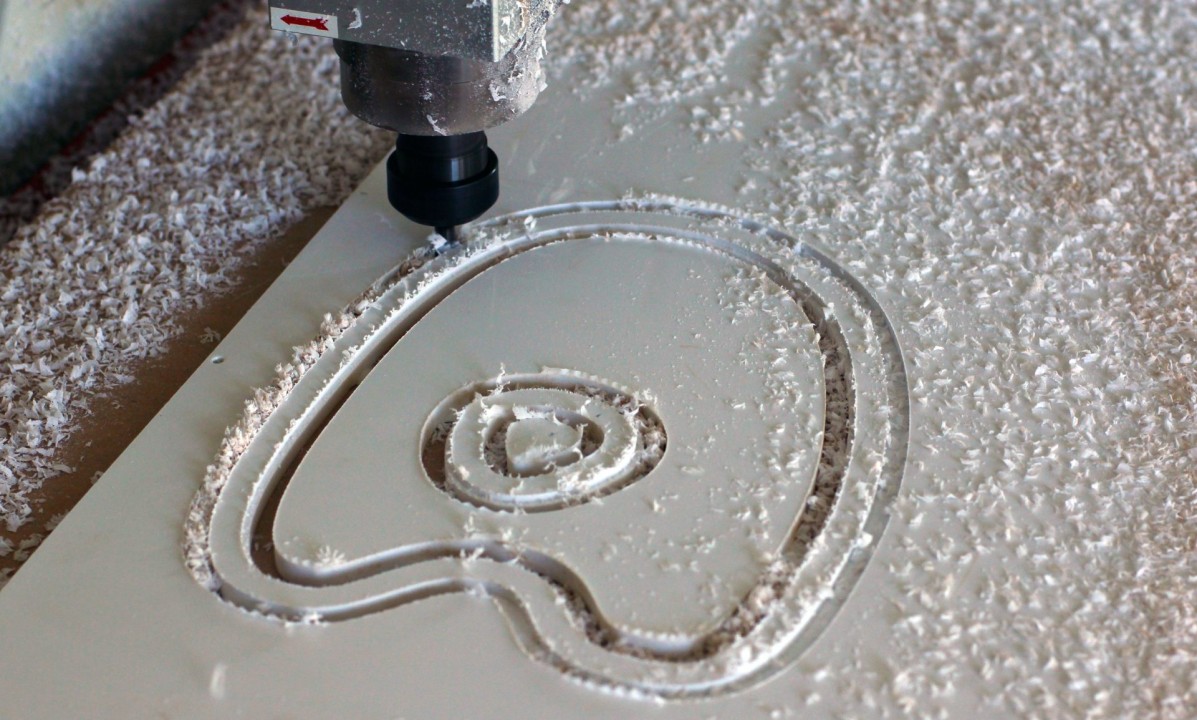

CNC Routing Services by Fuyu
Get quotes on custom parts with our Online CNC Routing Service. Make quick turn prototypes and production parts in days with free standard shipping on all US orders. ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified. ITAR registered.
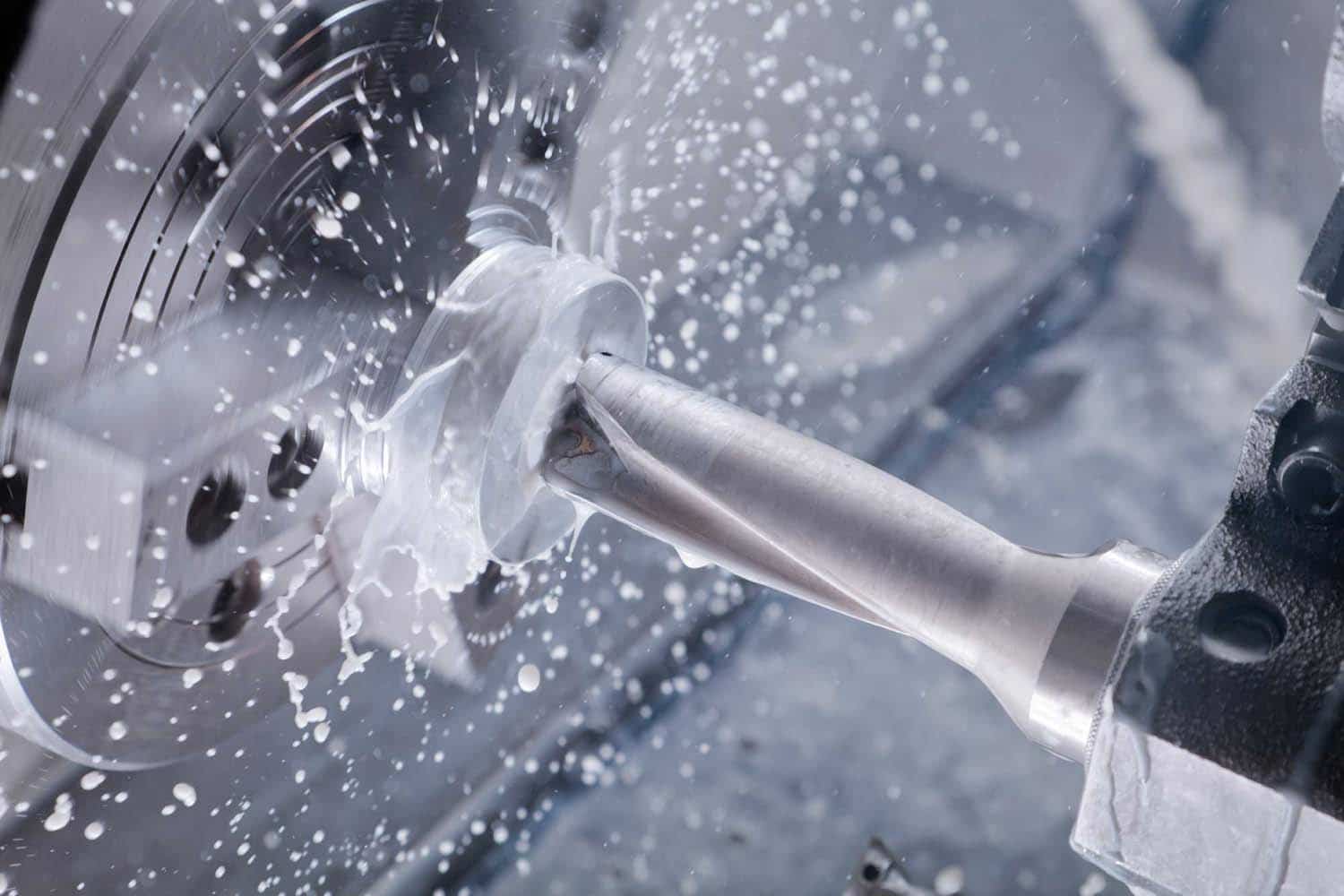

High Volume CNC Machining Services by Fuyu
High Volume CNC Machined prototypes and production parts in days | AS9100D | ISO 9001:2015 | ISO 13485 | IATF 16949:2016 | ITAR Registered | Free standard shipping on all US orders
CNC Machining Tolerances
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Part Size | Milled parts: 80” x 48” x 24” (2,032 x 1,219 x 610 mm). Lathe parts: 62” (1,575 mm) length, 32” (813 mm) diameter. |
| Standard Lead Time | Standard timeframe for completing machining orders: 5-15 business days. |
| General Tolerances | Metals: +/- 0.005″ (+/- 0.127 mm) in accordance with ISO 2768 unless otherwise specified. Plastics and composites: +/- 0.010”. |
| Precision Tolerances | Fuyu can achieve sub +/- 0.001″ tolerances based on drawing specifications and Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) callouts. |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.020” (0.50 mm), subject to variation based on part geometry and material selection. |
| Threads and Tapped Holes | Standard thread sizes are accommodated. Custom threads require manual quote review. |
| Edge Condition | Sharp edges are broken and deburred by default. |
| Surface Finish | Standard finish: as-machined, 125 Ra or better. Additional finishing options can be specified during quoting. |
Metal CNC Machining Materials
Aluminum 6061
Aluminum 5052
Aluminum 2024
Aluminum 6063
Aluminum 7050
Aluminum 7075
Copper 101
Copper C110
Copper C932
Copper 260
Copper 360
Nitronic 60 (218 SS)
Stainless Steel 15-5
Stainless Steel 17-4
Stainless Steel 18-8
Stainless Steel 303
Stainless Steel 316/316L
Stainless Steel 416
Stainless Steel 410
Stainless Steel 420
Stainless Steel 440C
Steel 1018
Steel 1215
Steel 4130
Steel 4140
Steel 4140PH
Steel 4340
A2 Tool Steel
O1 Tool Steel
Titanium (Grade 2)
Titanium (Grade 5)
Zinc Alloy
Plastic CNC Machining Materials
High-strength engineering plastic used for many commercial products.
A clear glass-like plastic. Good wear and tear properties. Great for outdoor use.
Acetal
Delrin 150
Delrin 100
Resin with good moisture resistance, high wear resistance, and low friction. Learn more about the difference between Delrin, PEEK, And Teflon/PTFE
High-density polyethylene is a moisture and chemical-resistant plastic with good impact strength. The material is outstanding for outdoor applications as well as watertight containers or seals.
Offers increased mechanical strength, rigidity, good stability under heat and/or chemical resistance.
With almost twice the tensile strength of ABS, polycarbonate has superior mechanical and structural properties. Used widely in automotive, aerospace, and other applications that require durability and stability.
PEEK
PEEK (USP Class VI TECAPEEK)
PEEK GF30
Offering excellent tensile strength, PEEK is often used as a lightweight substitute for metal parts in high-temperature, high-stress applications. PEEK resists chemicals, wear, and moisture.
Has excellent electrical properties and little or no moisture absorption. It carries light loads for a long period in widely varying temperatures. It can be machined into parts requiring chemical or corrosion resistance.
This material surpasses most plastics when it comes to chemical resistance and performance in extreme temperatures. It resists most solvents and is an excellent electrical insulator.
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. A general-purpose material. It offers a unique combination of wear and corrosion resistance, low surface friction, high impact strength, high chemical resistance, and does not absorb moisture.
Polyvinyl chloride (Type 1) is a highly chemical-resistant synthetic plastic, PVC is commonly in environments exposed to liquids or requires electrical insulation.
CNC Machining Finishes
The finish option with the quickest turnaround. Machined parts are left with visible tool marks and potentially sharp edges and burrs, which can be removed upon request. CNC machining surface finish is comparable to 125 uin Ra finish.
Learn more about standard machining surface finish.
The part surface is left with a smooth, matte appearance.
Learn more about Bead Blasting finish.
This is a batch-based process that tumbles vibrating media to remove sharp edges and burrs on CNC parts. Tumbling can remove machine marks on exterior surfaces. Parts over 8” may require a manual review.
Type II (MIL-A-8625, Type II) creates a corrosion-resistant finish. Parts can be anodized in different colors—clear, black, red, and gold are most common—and are usually associated with aluminum. Type III (MIL-A-8625, Type III, Class 1/2 “hardcoat”) is thicker and creates a wear-resistant layer in addition to the corrosion resistance seen with Type II.
Learn more about Anodizing finish.
Provides uniform nickel coating which offers protection from corrosion, oxidation, and wear on irregular surfaces. The finished part will be brighter. Thickness starts at .0001”. Conforms to MIL-C-26074.
Silver offers high solderability and electrical conductivity but is susceptible to tarnish. Conforms to AMS QQ-S-365D. Thickness is about 0.00002” – 0.0003.”
Provides corrosion resistance and good conductivity properties. Can be used as a base for paint. Can leave surface yellow/gold. Adds very little thickness, about 0.00001”-0.00004”. Chem film will conform to MIL-DTL-5541, TYPE I/II.
Improves corrosion resistance for 200 and 300 series and precipitation hardened corrosion-resistant steels. Thickness is negligible, about 0.0000001”. Conforms to ASTM A967, AMS-QQ-P-35, MIL-STD-171, ASTM A380, or AMS 2700.
This process is where powdered paint is sprayed onto a part and baked in an oven. This creates a strong, wear- and corrosion-resistant, more durable layer than standard painting methods. A wide variety of colors are available to create the desired aesthetic.
Learn more about Powder coating finish.
An electrochemical process cleans steel parts to reduce corrosion and improve appearance, by making the metal brighter. Removes about 0.0001”-0.0025” of the metal. Conforms to ASTM B912-02.
Learn more about polishing porcess.
Provides uniform zinc coating which offers protection from corrosion, oxidation, and wear on irregular surfaces. Conforms to ASTM B633-15.
Black oxide coating is a chemical conversion process used to blacken the surface of a part without adding a thick coating.
Learn more about Black Oxide Coating surface treatment
CNC Machining Design Guidelines
| Feature | Description | Details & Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Corner Fillets | Rounded transitions between internal corners to enhance strength and prevent stress concentration. | Design fillets with radii 0.020″ – 0.050″ larger than the standard drill size used for their creation. Maintain a drill diameter to depth ratio of 1:6 (recommended: 1:4) as a guideline for internal corner radii. This ensures proper tool access and avoids potential undercuts or tool breakage. |
| Floor Fillets | Rounded transitions at the base of features to improve flow and prevent sharp edges. | Design floor fillets with radii smaller than internal corner fillets to allow the same tool to clear material from the interior. This minimizes tool changes and optimizes machining efficiency. |
| Undercuts | Recesses or depressions designed into a part for functional or aesthetic purposes. | Always design undercuts using standard dimensions and away from corners to ensure accessibility for the cutting tool. This prevents tool interference and maintains dimensional accuracy. |
| Tapped/Threaded Hole Depth | Depth of a threaded hole for fastening components. | Provide tool clearance slightly beyond the tapped hole depth to ensure complete threads. This allows for proper tool engagement and avoids incomplete threads. |
| Complexity | Overall complexity of the design, impacting manufacturing costs. | Minimize the number of small cuts to reduce CNC machining costs. Design only essential features, balancing functional requirements with aesthetic considerations. This optimizes machining time and reduces material waste. |
| Material Selection | Choice of material based on application requirements. | Consider factors such as strength, machinability, and cost when selecting materials. Choosing materials with good machinability will reduce machining time and costs. |
Advantages and Challenges of CNC Machining
Precision and Repeatability: CNC milling and turning excel in delivering high accuracy and repeatability. Tight tolerances between +/-0.001″ – 0.005″ can be achieved, ensuring consistent part quality. This precision is crucial for applications demanding tight tolerances, such as aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
High-Volume Production & Flexibility: CNC machines can be programmed to operate continuously, enabling high-volume production runs. This makes CNC machining ideal for producing parts on demand, meeting both one-off and high-volume requirements. From custom prototypes to production runs exceeding 10,000 units, CNC machining provides the flexibility to scale production as needed.
Rapid Turnaround: CNC machining offers a rapid turnaround, enabling parts to be produced within a day, with delivery within a week. This speed is crucial for projects with tight deadlines or urgent needs.
Preserving Material Properties: Unlike processes like injection molding or additive manufacturing, CNC machining removes material through cutting, preserving the inherent mechanical properties of the chosen metal or plastic. This ensures that the machined parts retain their desired strength, durability, and other critical characteristics.
Material Versatility: CNC machining is compatible with a wide array of materials, including over 50 industrial-grade metals, alloys, and plastics. From aluminum and stainless steel to PEEK and ABS, CNC machining offers flexibility in material selection, allowing for diverse applications and design possibilities.
Geometric Complexity and Tool Access: While CNC machining offers great precision, geometric complexity can impact cost and feasibility. Simple, robust designs are generally more cost-effective to machine. Tool access limitations can restrict the complexity of features achievable, though multi-axis machines (5-axis and above) offer greater flexibility in machining intricate geometries.
Initial Setup Costs: Setting up CNC machining can involve significant initial costs, including training, programming, and tooling. However, these costs are fixed, meaning they can be spread across multiple parts, becoming more economical with increased production volume. Minimizing part repositioning during machining also helps optimize cost-effectiveness.
Material Limitations and Processing Time: Some CNC machining methods, such as wire EDM, can be slower and more expensive than other methods. Additionally, wire EDM requires electrically conductive materials, limiting its application range.
CNC Machining Applications
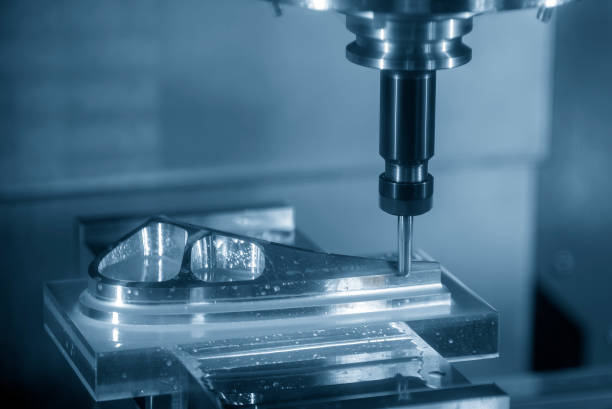

Rapid Tooling
CNC machining excels in creating durable tooling components, such as fixtures and molds. This is due to its ability to machine a wide range of dense materials like aluminum 5052 and stainless steel with high precision. CNC tooling solutions provide rapid turnaround times, enabling quick setup for production processes.
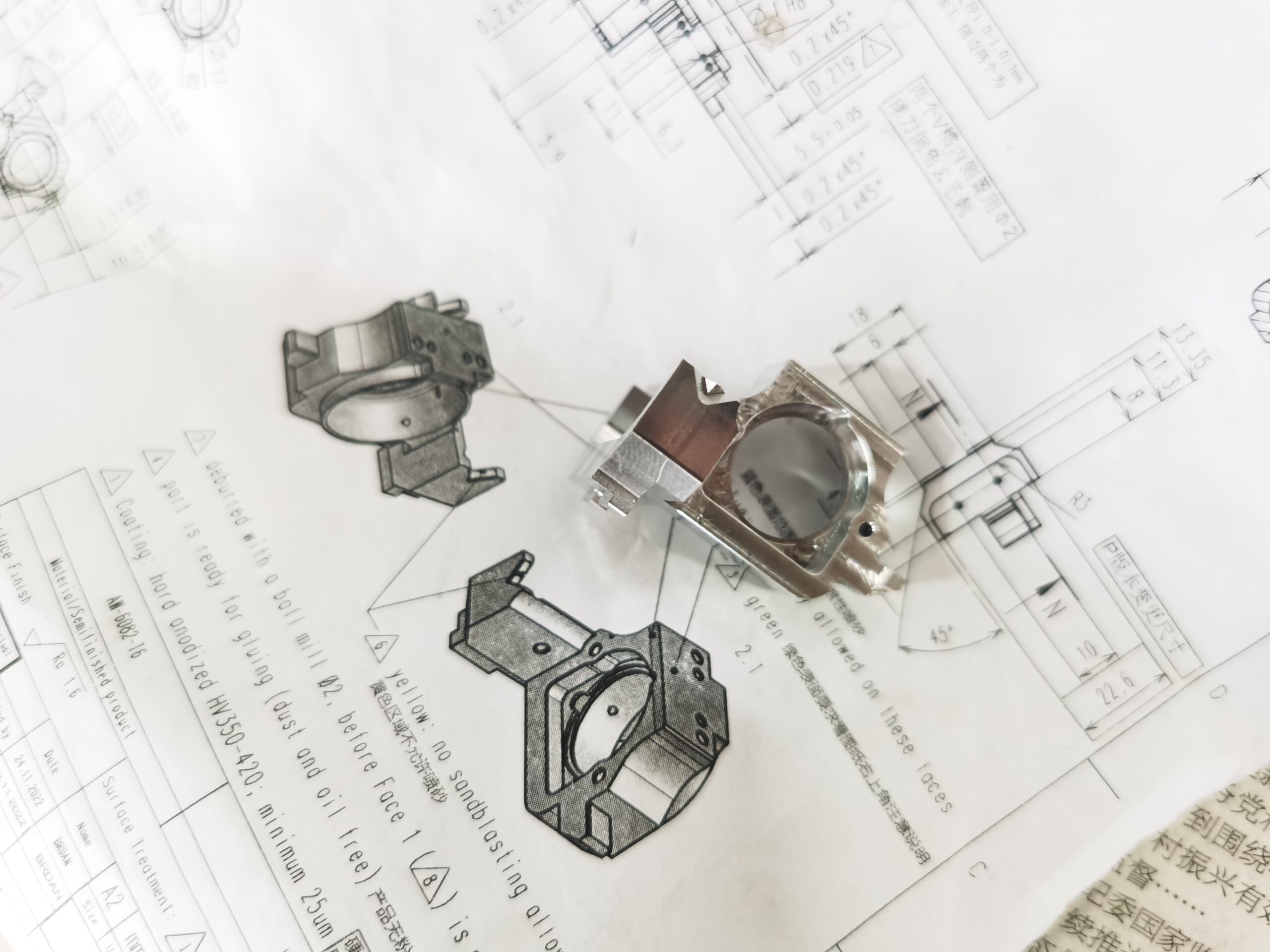
CNC machining is an ideal choice for rapid prototyping, thanks to its ability to work with a diverse range of materials, including affordable metal alloys like aluminum 6061 and plastics like acetal or ABS. The precision and speed of CNC machining, combined with the expertise of skilled machinists, enable quick and efficient prototyping iterations.
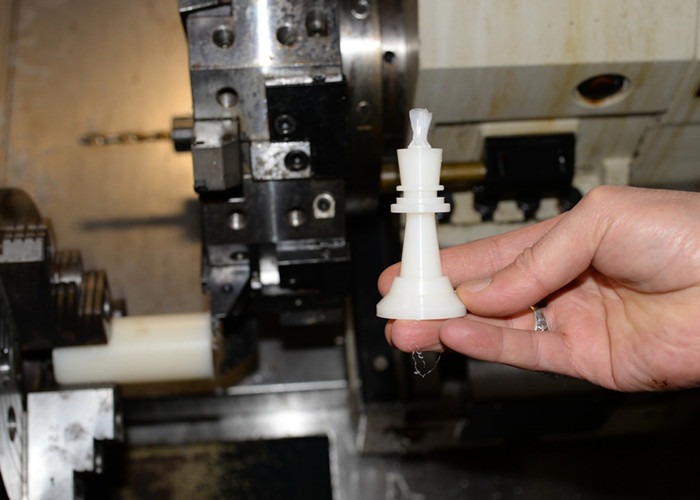

End-Use Production
CNC machining boasts performance-enhancing finishes, precision tolerances down to +/- 0.001″, and a selection of certifiable materials, making it an exceptional choice for producing high-quality end-use parts.
Conclusion
This article explored the unique characteristics of laser cutting and waterjet cutting, highlighting their individual strengths and providing guidance on which method is best suited for different applications. If you’re interested in learning more about these cutting technologies and how they can benefit your projects, contact a Fuyu representative for expert advice.
Fuyu offers a comprehensive range of manufacturing services, including sheet cutting and other value-added solutions, to support your prototyping and production needs. Access to article “sheet metal forming“ for additional information or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
FAQs – Custom Online CNC Machining Services
Q1: How does CNC machining work?
A1: CNC machining utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) to guide machine tools, such as mills and lathes, through precise movements. A CNC program, containing instructions for tool paths and cutting parameters, is loaded into the machine’s controller. The controller then directs the machine’s movements, ensuring accurate and repeatable machining operations.
Q2: How does CNC machining differ from traditional machining?
A2: Traditional machining relies on manual operation, where a skilled machinist controls the machine’s movements. CNC machining automates this process, utilizing a pre-programmed sequence to achieve high accuracy and repeatability. CNC machines offer greater precision, efficiency, and versatility compared to traditional methods.
Q3: What industries use CNC machining?
A3: CNC machining is widely employed across various industries, including: Aerospace, Automotive, Medical, Electronics, Defense and Consumer Goods.
Q4: What is the history of CNC machining?
A4: The origins of CNC machining can be traced back to the 1950s, with the development of computer-controlled machine tools. Early CNC machines were primarily used for military and aerospace applications. Over time, advancements in technology and software have made CNC machining more accessible and affordable, leading to its widespread adoption in diverse industries.
Q5: What are your inspection options for CNC machining?
A5: We offer a range of inspection options to ensure the quality and accuracy of our machined parts: Dimensional Inspection, Surface Finish Inspection, Visual Inspection and Functional Testing.
Q6: What are your CNC machining & turning capabilities?
A6: Our CNC machining capabilities include: Milling, Turning, Drilling, Tapping and Boring.
Learn more about our custom sheet metal capabilities, visit website: https://fuyutechnology.com/cnc-machining/


