Custom CNC Machining Services: Turning, Milling, and Routing
CNC machining, short for computer numerical control machining, stands as a widely adopted manufacturing technique that employs automated, high-speed cutting tools to shape designs from metal or plastic stock. This method utilizes various standard CNC machines, including 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines, lathes, and routers. The approach to cutting CNC parts may differ, as the workpiece might stay stationary while the tool moves, or vice versa, or both may move together.
What is CNC Milling?
CNC milling machines are engineered for precise manufacturing and repeatability, making them ideal for rapid prototyping and low-to-high volume production runs. These machines offer versatility, capable of working with various materials ranging from basic aluminum and plastics to more exotic ones like titanium. This flexibility makes CNC mills suitable for a wide range of tasks. To understand more about the distinction between a mill and a lathe and when milling is the preferred process, continue reading.
The Fundamentals of CNC Mills
CNC mills are automated cutting machines that utilize a rotating spindle-head to remove unwanted material. They come in various sizes and axis configurations to accommodate different manufacturing needs. While primarily used for cutting harder metals, CNC milling machines can handle workpiece materials spanning from plastic and aluminum to stainless steel and titanium.
How CNC Milling Functions
CNC mills excel at precision cutting of tougher materials. Like all CNC machines, a CNC mill is governed by G-Code generated through CAM software. The G-Code provides instructions to the machine on tool head movement, tool rotation speed, cutting depth, workpiece manipulation, and other parameters related to speed, feed rate, and coordination. The complexity of the G-Code depends on the number of axes the milling machine possesses.
While mills can still perform profile cutting of softer materials, CNC routers are more cost-effective for this purpose. The primary distinction between these machines lies in their operation: with a CNC router, the workpiece remains stationary while the router cutting head traverses around it, whereas a CNC mill may move both the tool head and the workpiece. CNC mills are predominantly utilized in industrial manufacturing, whereas CNC routing is more prevalent in lower output manufacturing such as woodworking.
Types of CNC Mills

3-Axis
The 3-axis CNC milling machine stands as the most prevalent type. Utilizing the full extent of the X, Y, and Z directions, it proves versatile for a broad spectrum of tasks.
4-Axis
This variant permits the machine to pivot on a vertical axis, enhancing its capability for continuous machining by repositioning the workpiece.
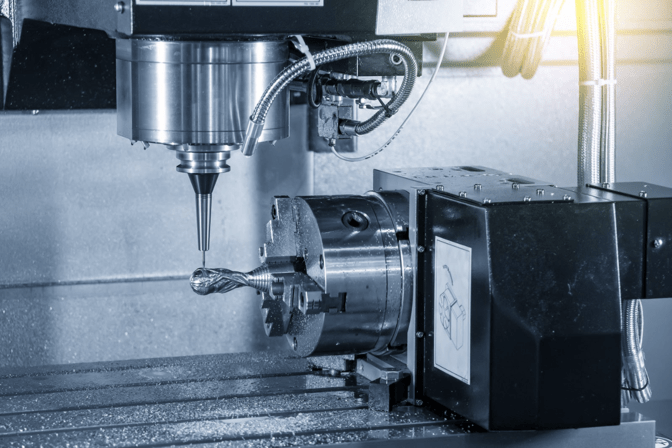

5-Axis
Incorporating three conventional axes alongside two supplementary rotary axes, the 5-axis CNC router boasts the ability to machine all five sides of a workpiece in a single setup without necessitating workpiece removal or repositioning. This configuration allows the workpiece to rotate while the spindle head maneuvers around it. However, these machines are larger and come with a higher price tag.
What is CNC Turning?
Understanding CNC Lathes
A CNC lathe, also known as a live tooling lathe, excels in shaping symmetrical cylindrical or spherical parts. Typically, the lathe rotates a workpiece on either a vertical or horizontal axis, while a stationary cutting tool moves along a linear path to shape the workpiece. This process of shaping a workpiece on a CNC lathe is known as turning.
How CNC Turning Operates
CNC lathes utilize a subtractive approach to shape the desired geometry. After generating G-Code instructions, a raw bar of material is loaded into the lathe’s spindle chuck. The chuck secures the workpiece in place while the spindle rotates. Once the spindle reaches the required speed, a fixed cutting tool is brought into contact with the workpiece to remove material until the desired shape is achieved.
Various operations can be executed on a live tooling lathe, including facing, threading, knurling, drilling, boring, reaming, and taper turning. Each operation may necessitate tool changes, potentially increasing setup time and cost.
Upon completion of all machining operations, the part is separated from the stock material for further post-processing. Subsequently, the CNC lathe is prepared to repeat the operation with minimal to no setup time between cycles.
Types of CNC Lathes
Numerous lathe variants exist, but the most prevalent are 2-axis CNC lathes and Swiss-type lathes. Swiss-type lathes differ in that stock material is fed through a guide bushing, allowing the cutting tool to operate closer to the point of support. This feature proves beneficial for manufacturing long, slender CNC lathe parts and micro-machining tasks. Certain Swiss-type lathes are equipped with a secondary tool head, enabling them to perform multiple machining operations without relocating the workpiece to another machine. This capability renders Swiss-type lathes highly cost-effective for producing intricate turned parts via CNC lathe services.
Advantages of CNC Turning
Similar to CNC mills, CNC lathes offer easy setup for achieving high repeatability, making them suitable for rapid prototyping as well as low and high-volume production runs. Multi-axis CNC turning centers and Swiss-type lathes allow for performing multiple machining operations in a single machine, thereby reducing the need for multiple machines or tool changes typically associated with traditional CNC milling setups, especially for complex geometries.
What Is CNC Routing?
CNC routing, short for computerized numerical control routing, is a subtractive manufacturing technique that employs computer-controlled machines to carve and shape various materials, typically wood, plastic, or metal. It utilizes a rotating cutting tool known as a router, guided by precise digital instructions, to craft intricate and accurate cuts, holes, and contours in the material. CNC routing shares similarities with other CNC processes like CNC milling and CNC turning, as they all rely on computer-controlled machines and adhere to a similar operational sequence. However, there are distinct differences outlined below:
Cutting Tool: In CNC routing, the primary cutting tool is a rotating router bit, whereas CNC milling typically employs a rotating multi-point cutting tool called an end mill. CNC turning, conversely, utilizes a single-point cutting tool for shaping cylindrical components.
Material Orientation: CNC routing machines are typically designed to handle flat or sheet materials, such as plywood or acrylic sheets, secured to a worktable. In contrast, CNC milling and turning processes often involve block or cylindrical workpieces.
Cutting Direction: CNC routing machines primarily operate along the X and Y axes, cutting within the material’s plane. In contrast, CNC milling and turning machines can move in multiple axes, allowing for more intricate three-dimensional machining.
Applications: While there may be some overlap, CNC routing is often linked with applications requiring large-scale cutting, such as furniture manufacturing, sign production, and cabinetry. CNC milling is commonly utilized for precise and detailed part machining, while CNC turning excels in producing cylindrical or rotational components like shafts and connectors.
Despite these distinctions, all CNC processes offer the benefits of precision, repeatability, and the capacity to fabricate complex shapes with minimal manual intervention. They enhance efficiency, reduce labor expenses, and enable the consistent production of high-quality outcomes.
Applications of CNC Routing
CNC routing finds widespread use across various industries for fabricating finished parts and production components. Here are some specific applications of CNC routing:
Wooden Furniture
CNC routing is extensively utilized in crafting wooden furniture. It enables precise cutting, shaping, and detailing of diverse wood types, facilitating the creation of intricate designs, decorative patterns, and seamless edges. CNC routers excel at producing components like table legs, chair backs, elaborate panels, and ornamental accents with exceptional accuracy and efficiency.
Signage
CNC routing is commonly employed in the signage industry for businesses, organizations, and events. It allows for the precise cutting of materials such as wood, plastic, and metal to fashion custom shapes, letters, logos, and embellishments. CNC routing achieves intricate detailing, sharp edges, and uniform outcomes, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor signage applications.
Molds for Thermoforming
Thermoforming, a manufacturing process involving heating a plastic sheet and shaping it over a mold, relies on CNC routing for mold creation. By precisely cutting or carving materials like wood or composite boards, CNC routers produce molds with intricate shapes and contours, ensuring accurate and repeatable plastic sheet forming for various applications like packaging, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Cabinetry and Millwork
CNC routing plays a significant role in crafting cabinetry and millwork components. It facilitates precise cutting, shaping, and detailing of materials like wood, MDF, or plywood, enabling the fabrication of intricate cabinet doors, drawer fronts, moldings, and decorative panels.
Prototyping and Product Development
CNC routing is widely adopted for prototyping during product development phases. It enables the rapid and precise production of items, allowing designers and engineers to evaluate and refine their designs before proceeding to full-scale production. CNC routers fabricate prototypes from various materials, including plastics, foam, wood, and composites.
Engraving and Personalization
CNC routing machines equipped with specialized engraving bits engrave intricate designs, text, logos, or images onto a variety of materials. This capability makes CNC routing ideal for crafting personalized items such as plaques, awards, signs, nameplates, and customized artwork.
Automotive and Aerospace Components
CNC routing finds application in manufacturing automotive and aerospace components. It shapes and trims parts made of materials like aluminum, carbon fiber, plastics, or composites. CNC routers deliver precise cuts and contours necessary for components such as dashboards, interior panels, exterior trim pieces, and various aircraft parts.
FAQs – Custom CNC Machining Services
The Difference Between CNC Turning and Milling
In simple terms, the distinction between CNC turning and milling lies in which component moves during the process – either the machine or the raw material. In CNC milling, the material remains stationary while the cutting tools rotate around it. Conversely, CNC turning involves keeping the tools stationary while swiftly rotating the material to achieve the desired shape.
Is CNC milling machine the same thing as CNC routing machine?
No, CNC milling machines and CNC routing machines are not identical, although they share certain similarities.
CNC milling machines are employed to eliminate material from a workpiece to form a specific shape or pattern. They function by rotating a cutting tool that penetrates the workpiece.
In contrast, CNC routing machines are utilized to cut and shape materials such as wood, plastic, and foam. They function by moving a cutting tool along multiple axes to create the desired form.
Despite both machines being computer numerically controlled (CNC) and automating the cutting process, they are tailored for distinct applications and possess unique capabilities.
Do you offer Quick-Turn CNC Machining Services?
Yes, Fuyu provides quick lead times for quick-turn parts, with many parts available within 7-15 days. We offer an expedite option, and our team collaborates closely with you to meet urgent deadlines.
Feel free to reach out to us with any further inquiries or to discuss your specific prototyping requirements!


